Ethereum under the hood- Part 8( Blocks -2 )

Welcome back, we start right where we left off with a little deeper dive into blocks, and for those who are following Ethereum 2.0 I would recommend reading this, For this section about Blocks Part 2, we cover:
- Quick review
- Bloom filters/LogsBloom Field
- Genesis Block
- Summary
- Next
Quick Review:
As a regular practice in this series, a quick overview of Part -7

BloomFilters and LogsBloom Field:
In Chapter-7, we discussed Ethereum Block header fields; one among them is Field-8: logsBloom. We will try to answer two questions and throw some light into Bloom Filters. Let us focus on two issues 1. Why is this Field needed? 2. What is a Bloom Filter?
- Why is this Field needed?: Ethereum is a forward-only global state machine with financial and non-financial transactions on a central database. These transactions required to be recorded with some labels to search quickly and efficiently. These events are searchable with results as soon as possible. Each Blockheader contains the logsBloom Field, which includes the complete information of the entire set of events/logs in just one Field. Below is an excellent description of the need for this Field.

LogsBloom field[2048 bytes ] from an Ethereum Block, notice the “1” is at position:212, and “2” is at position:233, we will revisit this topic in BloomFilter.
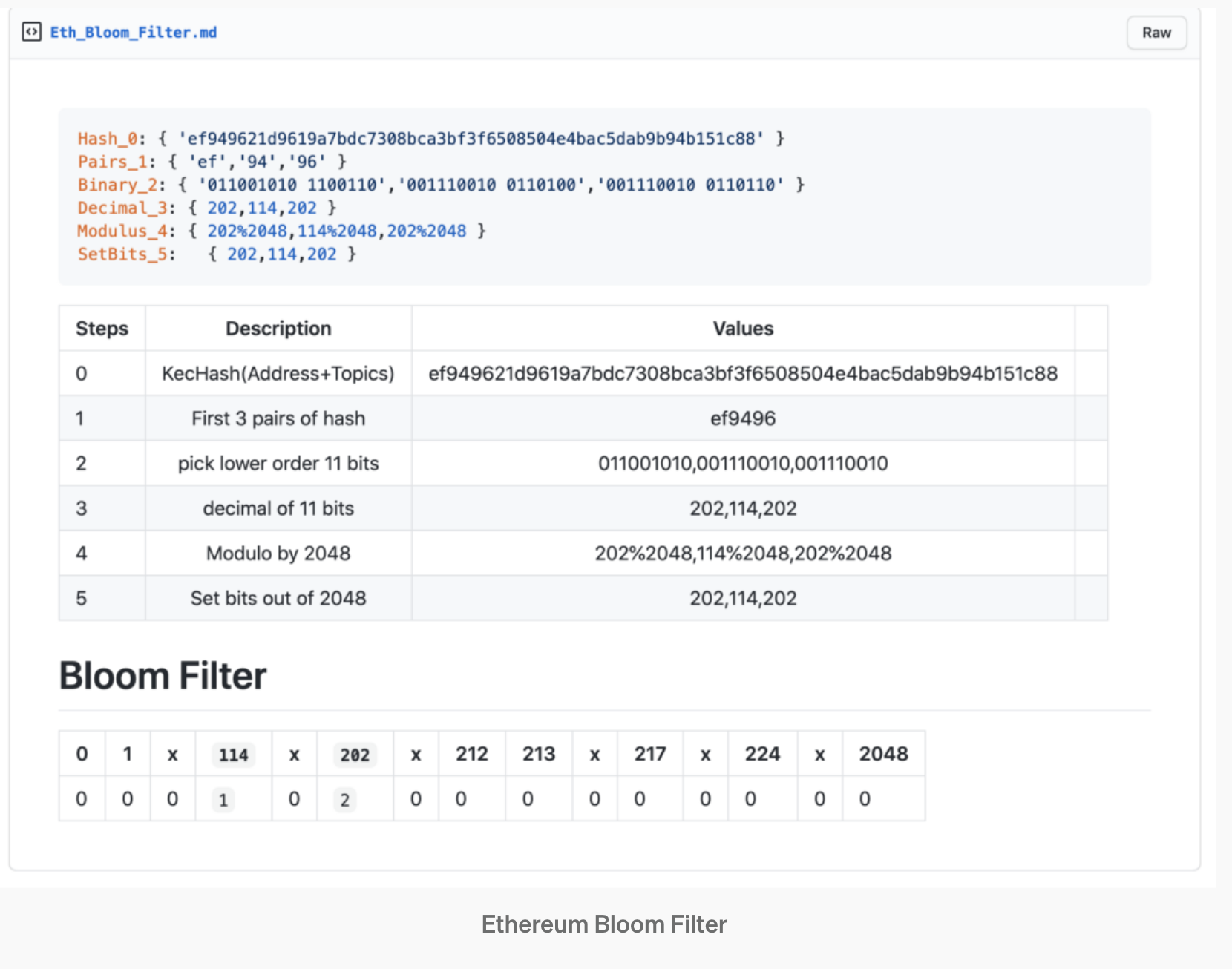
logsBloom[2048]:"0x00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001000000000000000000002000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000008000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000........0"2. What is a Bloom Filter?: Now that we have an idea of the logsBloom Field, let us explore Bloom filters. Ethereum chose the Bloom Filter algorithm for its speed and effectiveness of the probabilistic data structure. There can be thousands of events in a Block and going by our regular theme of the need for speed for lookup speed; it seems that Bloom filters were a suitable choice. Ethereum implements a custom bloom filter as defined in the yellow paper :

Let us work through the specs with an example below.
Dig Deeper:

Genesis Block:
Now that we have a little bit of understanding of what Blocks are, we can now explore Genesis Block. Almost all Cryptocurrency projects have a “Genesis” synonym to the Beginning, let us recall that Ethereum is a World state+Virtual machine and state 0 is the Genesis State, which has a pre-defined set of values as agreed upon by all participants within the Ethereum ecosystem. Ethereum Yellow paper defines the preset values of the Genesis Block.
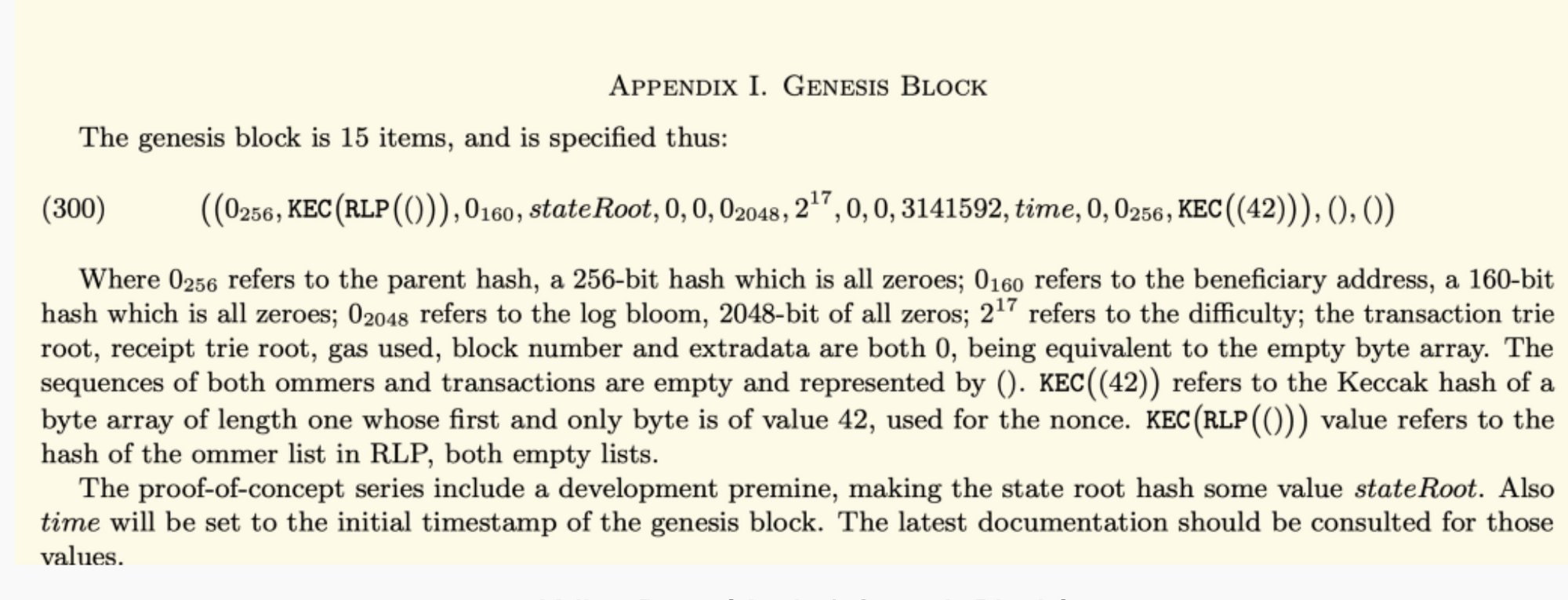
A Genesis Block using Elixir with some random values, notice the name of the fields and their corresponding values(Fig:1)
Genesis Block
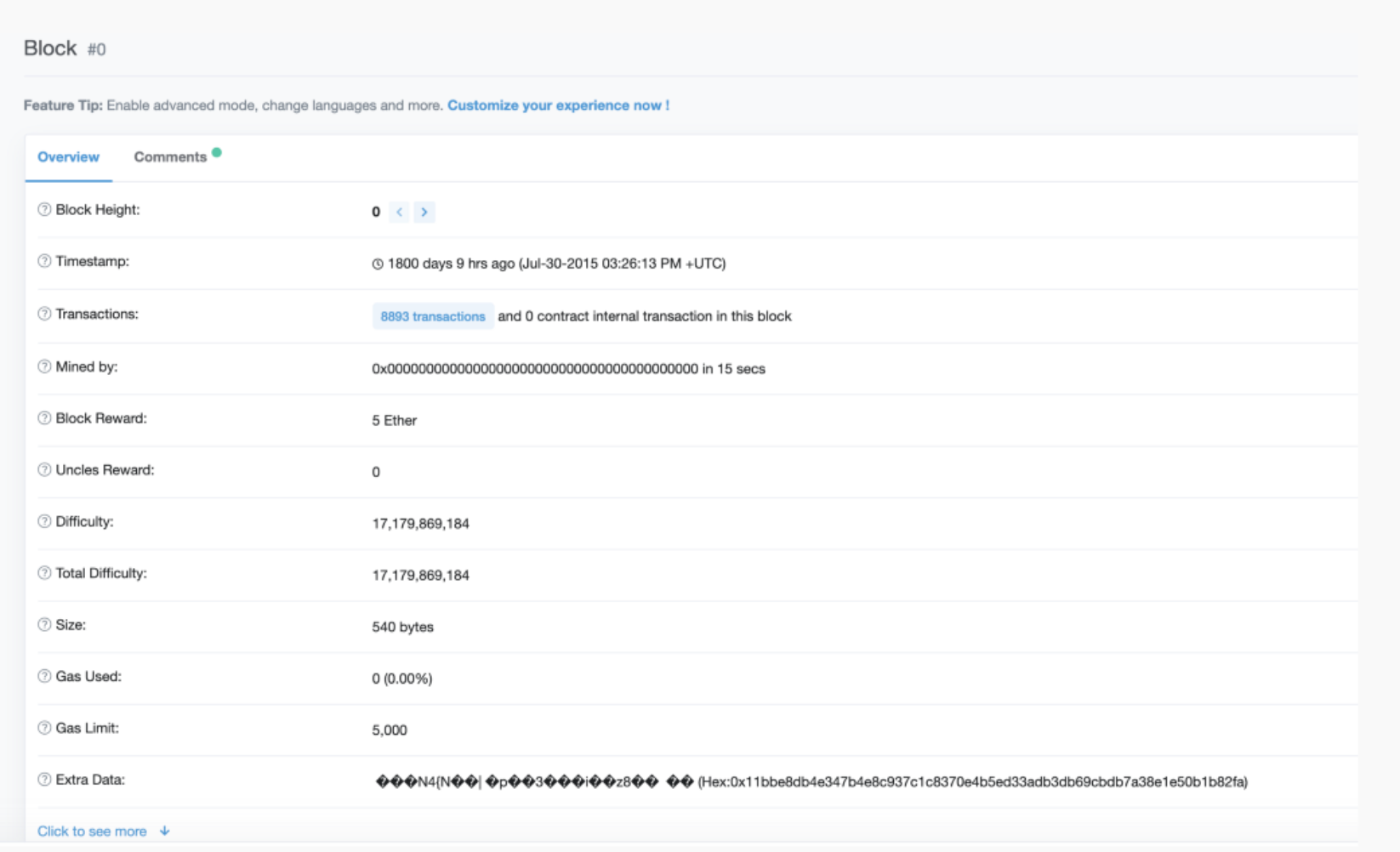
Take a peek at the Genesis Block to see if this matches with the yellow paper specification
Summary:
- LogsBloom is a Block Header field.
- LogsBloom field is a global event indicator for the Block Header.
- Bloom Filter algorithm is the mechanism for the LogsBloom field.
- Ethereum specifies a specialized Bloom Filter algorithm.
- A Genesis Block is the Block 0 state of the Blockchain.
- Genesis Block has pre-defined values, agreed by the ecosystem.
References:






